陆地水储量是水资源可用性的综合指标,对保障水资源的可持续发展至关重要,干旱直接影响水资源的供给和质量,进而影响生态系统的健康和人类的生活。在干旱条件下,陆地水储量的稳定性显得十分重要,对其稳定性进行评价具有重要科学意义。因此,为探究全球陆地水储量对干旱的响应,识别未来全球陆地水储量的脆弱区,并给出相应的对应策略显得十分重要。
近日,地理与环境科学学院魏伟教授研究团队联合中科院西北生态环境资源研究院、澳大利亚科廷大学、阿联酋阿拉伯联合酋长国大学等多家科研单位,以CMIP6的5个不同情景(History、SSP1-2.6、SSP2-4.5、SSP3-7.0和SSP5-8.5)的地表温度(LST)、叶面积指数(LAI)和降水(P)数据,利用空间距离模型,概率分布函数和累积分布函数,构建了全新的标准化温度植被降水指数(STVPI),在多角度验证该指数科学、有效性的基础上,利用该指数监测了全球干旱状况,该指数也被用于监测全球干旱状况和调查陆地储水量(TWS)的抗旱稳定性。在干旱条件下,陆地水储量的稳定性显得十分重要,对其稳定性进行评价,进而探究全球陆地水储量对干旱的响应,用以识别未来全球陆地水储量的脆弱区具有重要价值。
相关研究成果以“Assessing the stability of terrestrial water storage to drought based on CMIP6 forcing scenarios”为题在线发表于《Journal of Hydrology》期刊上,魏伟教授和王旭峰研究员为论文共同第一作者,王继平为通讯作者。该研究得到了国家自然科学基金(42261023和41861040)的共同资助。
论文链接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2024.132232
附主要成果图:
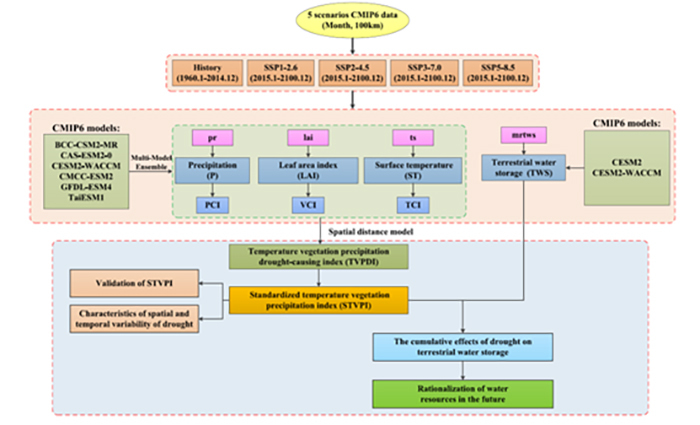
Fig. 1. The technical plan of this research.
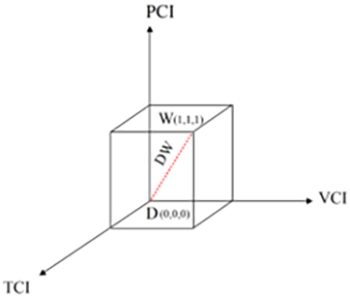
Fig. 2. 3D spatial distance model for TCI, VCI and PCI.
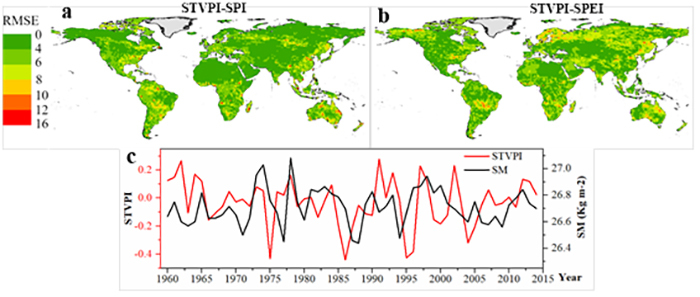
Fig. 3. Accuracy validation of STVPI and TWS. a and b are RSME of STVPI with SPI and SPEI at spatial scales, respectively. c is a linear trend fit of STVPI and SM from January 1960 to December 2014.
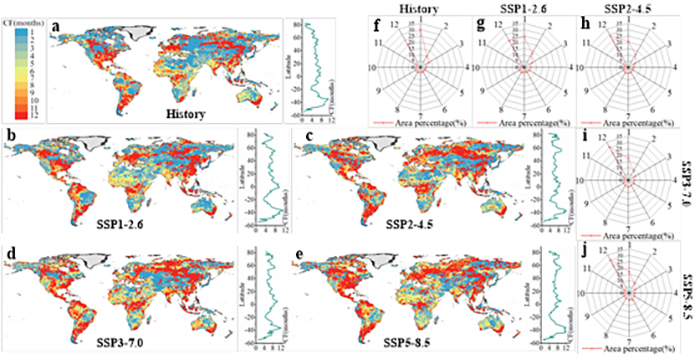
Fig. 4. Cumulative effect of drought on TWS. a-e are the spatial distribution of the cumulative effect of drought on TWS for each scenario, and f-g are areas of different cumulative effect as a percentage of the land surface area for each scenario.
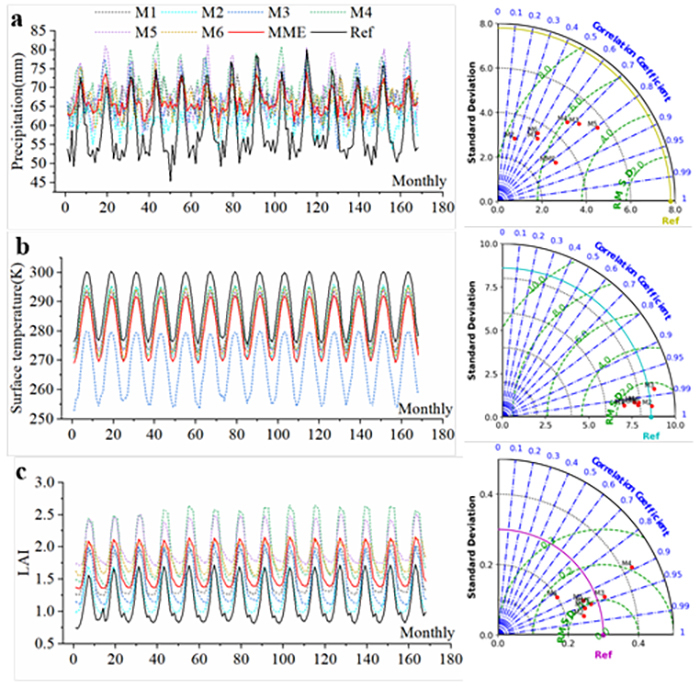
Fig. 5. CMIP6 models sensitivity in historical periods (2001.1-2014.12).From M1 to M6 are BCC-CSM2-MR, CAS-ESM2-0, CESM2-WACCM, CMCC-ESM2, GFDL-ESM4 and TaiESM1 respectively.In the Taylor diagram, the closer the distance between the model and Ref, the better the performance of the model. Ref is the reference value of precipitation, surface temperature and leaf area index.MME is the result of CMIP6 multi-model integration.
近年来,魏伟教授团队在干旱遥感领域取得了一系列成果,围绕干旱事件长时序重建、植被对干旱的响应、陆地水储量与干旱的时空关系等开展了研究,代表性成果列举如下:
Wei Wei, Sufei Pang, Xufeng Wang, et al. Temperature vegetation precipitation dryness index (TVPDI)-based dryness-wetness monitoring in China[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2020, 248: 111957. Wei Wei , Jiping Wang , Xufeng Wang, et al. Assessing the stability of terrestrial water storage to drought based on CMIP6 forcing scenarios[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2024.645.132232
Wei Wei, Jiping Wang,Xufeng Wang, et al.The response of global terrestrial water storage to drought based on multiple climate scenarios[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2024303:107331
Wei Wei, Jing Zhang, Junju Zhou, et al.Monitoring drought dynamics in China using Optimized Meteorological Drought Index (OMDI) based on remote sensing data sets[J].Journal of Environmental Management,2021,292:112733.
Wei Wei , Haoyan Zhang, Libang Ma, et al. Reconstruction and application of the temperature-vegetation-precipitation drought index in mainland China based on remote sensing datasets and a spatial distance model[J].Journal of Environmental Management,2022, 323,116208
Wei Wei,Ting Liu, Liang Zhou, et al. Drought-Related Spatiotemporal Cumulative and Time-Lag Effects on Terrestrial Vegetation across China[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(18): 4362.

